Hernia
What is a hernia?
A condition in which part of an organ bulges through an abnormal opening. It is caused by a combination of
- pressure; and
- an opening or weakness of muscle.
What are the signs and symptoms?
- Bulge or lump, especially when you strain, getting bigger over time.
- Pain or discomfort
- Heavy or dragging sensation
- Occasionally life-threatening complications such as bowel obstruction and perforation when the hernia contents are strangulated or incarcerated
Is hernia surgery necessary?
Hernia will not resolve on its own. A painless small hernia can be left alone however it may worsen with time. Surgery can resolve the symptoms and prevent the hernia from becoming bigger and causing life-threatening complications.
What are the surgical options?
Surgical repair will depend on the type of hernia. In general, the hernia is repaired with a mesh, either laparoscopically (key-hole) or by open technique. We off other highly specialized techniques such as Botox injection and component separation for better outcomes in large complex hernia.
How soon will I recover?
You should be able to go home the same day or the following day. Longer stay may be required in large, complex or complicated hernia. You should also be able to return to normal activities within 1-2 days and return to work after 1-2 weeks. Strenuous activity/ work/ exercise will be recommended 4-6 weeks of recovery time.
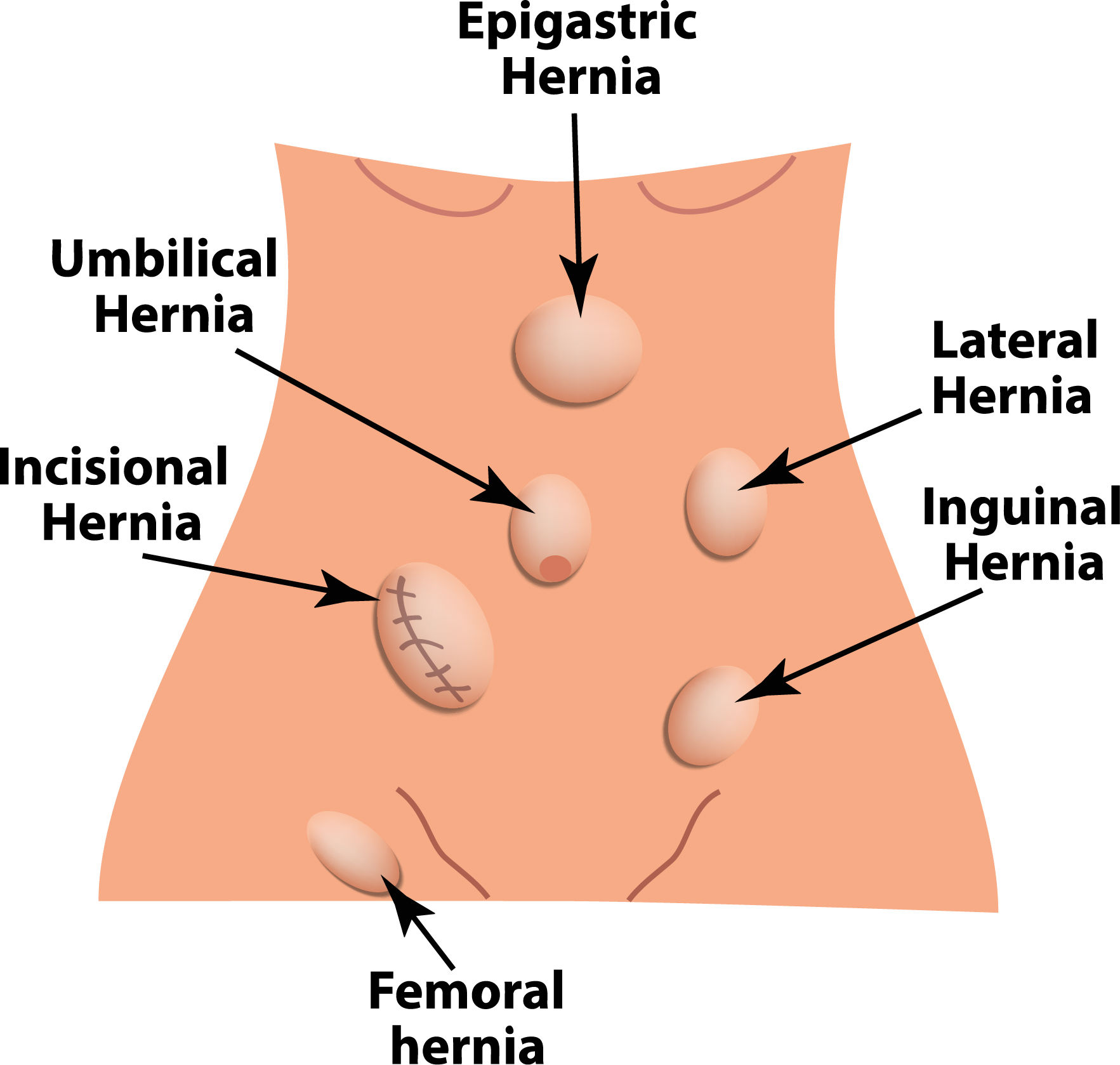
Types of hernia:
- Inguinal hernia
- Femoral hernia
- Umbilical hernia
- Epigastric hernia
- Incisional hernia
- Strangulated/ Incarcerated hernia
- Recurrent hernia
- Rare herniae : spigelian, lumbar, obturator.
Inguinal Hernia
The most common hernia. It is a weakness of the muscles in the groin region which allows the abdominal contents to protrude.
Femoral Hernia
A less common hernia seen in the groin region, sometimes difficult to differentiate from the inguinal hernia. Most often seen in elderly women. Femoral hernia should generally be treated as it carries a much higher risk of complications if left untreated.
Umbilical Hernia
A bulge occurring in the belly button(umbilicus) due to a defect in the underlying muscle.
Epigastric Hernia
A bulge in the midline between the belly button and sternum (breastbone).
Incisional Hernia
A bulge or lump that occurs in the previous surgical scars/wounds due to the weakness in the muscle layers in that site.
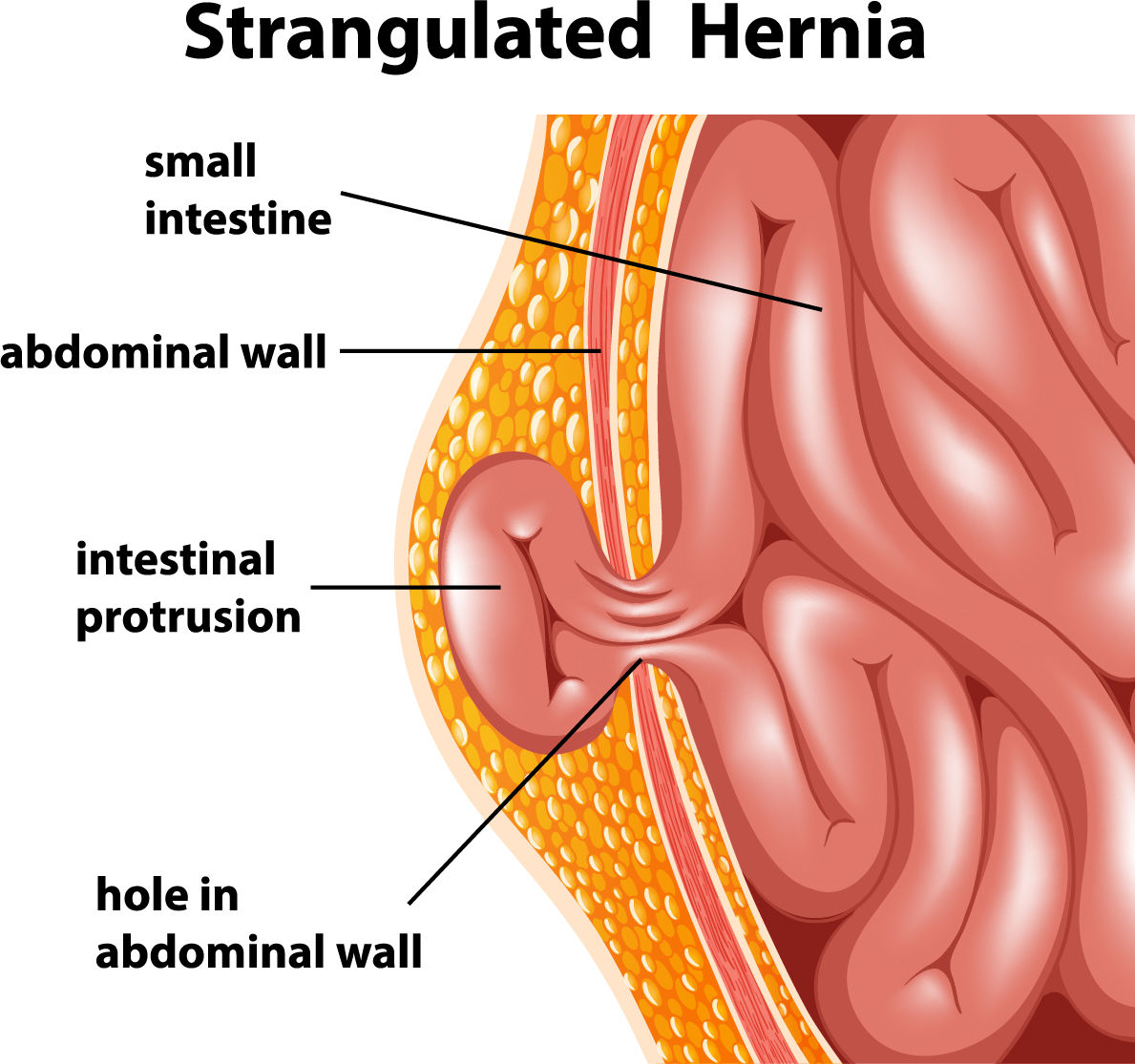
Strangulated/ Incarcerated Hernia
In these hernia, the blood supply is cut off due to the tight hernia defect. The protruding organs generally the intestines will suffocate due to lack of blood supply. This is a surgical emergency, where the hernia repair has to be performed as an emergency. This condition can be life-threatening with potential intestinal perforation and sepsis.
Recurrent Hernia
A bulge that recurs in a previously repaired hernia. Fortunately this is rare, less than 3%
 |  |